Psoriasis is a chronic variant of dermatopathology, characterized by the formation of reddish-silver papular eruptions in various parts of the body. It is most often formed in children's age group, but may initially occur after 20-35 years.
Causes of occurrence:
- metabolic disorders;
- gastrointestinal tract pathology;
- dysbiosis;
- chronic stress situations;
- presence of negative habits, for example, alcohol abuse.
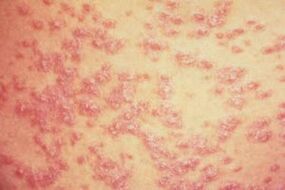
Since the skin is a single giant organ, the appearance of multiple skin eruptions, including those of a psoriatic nature, requires diagnostic studies and an integrated therapeutic approach.
Diet therapy is a significant factor on the way to getting rid of unsightly formations. The correct diet in combination with drug therapy are the main guidelines of modern methods of influencing the disease.
The most important thing to monitor while maintaining adequate nutrition for psoriasis is to drink a large enough amount of water a day, seven to ten glasses. The liquids used must be of high purity and, in the case of juice consumption, it is recommended to cook them freshly squeezed.
The Basics of Proper Nutrition
Each person's body is unique, so a specialist must select a diet that is appropriate in each strictly individual case - there is simply no one-size-fits-all menu for all people with psoriasis.
The main task of diet therapy in identifying the pathology is to maintain an adequate acid-base environment in the patient's body. The balance should tip in favor of an alkaline medium, as an acid only aggravates the course of the pathology. Experts recommend that you include 2 to 4 times more alkaline foods in your diet.
Basic principles:
- eat fractionally - in small portions, 4-5 times a day;
- consume 2 - 2. 5 liters of liquid per day;
- adjust the diet so that the intestines are not overloaded;
- timely emptying of the intestines is the foundation of health, carefully monitoring the opportunity for the release of toxins;
- at the time of exacerbation of the pathology, it is recommended to enrich the body with mineral acids and organic elements: not more than 20%, the rest must be alkaline products;
- maximum rejection of alcoholic beverages, tobacco products;
- reduce the amount of table salt in the diet;
- minimize the use of preservatives, emulsifiers, dyes, stabilizers and disintegrants;
- avoid all citrus fruits in the diet as much as possible - in addition to oranges, lemons and grapefruit are also included in this subgroup;
- emphasis should be placed on the use of fermented cereals and dairy products, vegetable oils - but also in small quantities.
Adhering to the above principles helps to reduce the number of psoriasis exacerbations to a minimum, to achieve long periods of disease remission.
What should be discarded
During the consultation, the specialist will especially emphasize that you cannot eat with psoriasis. Diet therapy provides maximum rejection of the individual product list, but necessarily provides a complete diet that provides the patient with all the nutrients.
What is recommended to refuse:
- Numerous studies carried out by experts among people suffering from psoriatic eruptions have convincingly shown that spices cause an exacerbation of the disease. The maximum concentration of essential oils and aromatic elements in them is very harmful for people with dermatopathology - it leads to an itchy feeling in the skin, a debilitating burning sensation and an aggravation of the pathology.
- A variety of nuts have a similar negative effect on the skin. The most allergenic product is peanuts. It is recommended to avoid as much as possible the nuts in their pure form and in the form of various additives. Peanut butter is completely removed from the diet.
- A variety of spicy, smoked and canned foods have a particularly irritating effect on the tissues of the intestinal loops. They irritate the mucous membrane and prevent proper processing and nutrient absorption. It is what leads to the appearance of new defects in the dermis - psoriatic plaques and scales.
- A significant percentage of essential oils toxic to psoriasis patients is also found in citrus peel. That's why experts recommend that you refuse to include not only the fruits themselves, but also their juices in the diet, since with the industrial method of production you squeeze without removing the zest.
- Inflammatory manifestations in the dermis can also be caused by arachidonic acid, which is saturated with meat. When preparing the menu, preference is given to white varieties, for example, turkey and rabbit meat.
- The most extreme limitation is imposed on grape-based alcoholic beverages. It is during fermentation that aromatic compounds are formed, which have the most negative effects on the state of the dermis. The structures of the liver also suffer, the filtering capacity of the organ generally decreases, toxins and toxins build up - psoriasis is exacerbated.
A well-designed diet also leads to the normalization of a person's weight; a complication of psoriasis such as arthritis can go away for a long time if the person adheres to the basic nutritional recommendations received from a specialist during an appointment.
Approved Products
The opinion of dermatologists around the world is unanimous - you should not rush to extremes and limit yourself severely on nutrition. Before adjusting your diet, a specialist will perform a variety of diagnostic procedures to identify the foods that affect you most negatively. Based on this, a decision will be made about what can be ingested with psoriasis for that particular person.
The following elements have a positive effect on the skin's condition:
- a variety of unsaturated omega-3 fatty acids. Natural arachidonic acid antagonists, they, being in marine fish, have the best effect on the dermis;
- a variety of vegetables contain vitamins and caratinodes - they optimally affect the protective barriers of the human body, multiply the activity of immune structures, contribute to maximum resistance to negative external factors that can provoke an exacerbation of dermatopathology;
For those suffering from psoriatic rashes, it is helpful to:
- add lecithin in the form of granules to the diet;
- replacing coffee and coffee-based beverages with medicinal teas;
- eat more variety of vegetables;
- drink freshly squeezed juices more often;
- abandon artificial flavoring options as much as possible - replace them with newly grown herbs;
- it is helpful to include fresh fruit in the diet: gooseberries and viburnum, mountain ash and gooseberries, blueberries;
- a variety of cereals will bring maximum benefit - oats, buckwheat, millet;
- sea fish should be on the table at least 4-5 times a week, but steaming is recommended;
- poultry dishes are allowed up to 3-4 times in the current week, carefully removing all the skin;
- milk and dairy products are allowed only those with a reduced fat and table salt content;
- eggs should be boiled - 3-4 times a week;
- of oils are acceptable - olive, cottonseed, corn.
Thus, the psoriasis diet is based on the use of simple, varied and highly fortified foods.
starvation
An indispensable condition for a complete therapeutic psoriasis diet is the obligatory cleansing of the human body - curative fasting helps in this. The person is advised to select a day in their schedule during which only distilled liquid will enter their body.
The next day, vegetable salad is allowed for breakfast, the use of monastery tea - and again following the menu compiled from the daily diet.
The result of curative fasting and careful observance will be maximum - after 20-35 days the person will feel an overall improvement in well-being, the skin will clear faster.
Frequent fasting should not be practiced - follow the gold standard: no more than 1 cleansing day per week. A variety of cleansing procedures, practiced in beauty salons, are also prohibited - they will only disturb the natural balance of the intestinal loops and therefore suffer from psoriasis.
Clean, radiantly beautiful skin is a possible outcome, even with a diagnosis of psoriasis. The main thing is to adhere to dietary therapy designed individually by a specialist, in combination with medications - as needed.























